How Vara Network Stands Out: A Deep Dive into Its Consensus, Governance, and Developer Ecosystem
Table of contents
- Introduction: Vara Network’s Cutting-Edge Approach
- Comparing Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms: PoW vs. PoS vs. NPoS: Why NPoS Leads the Way
- 2) Governance: Vara’s OpenGov Framework
- 3) Gear Protocol and WebAssembly (WASM) vs. Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
- 4) Actor Model for Communication
- 5) Rust Programming Language vs. Solidity and Move
- Conclusion: Why Vara Stands Out
Introduction: Vara Network’s Cutting-Edge Approach
Vara Network is redefining blockchain with its innovative Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS) system, offering enhanced speed, scalability, and eco-friendliness compared to traditional Proof of Work (PoW) blockchains. Its OpenGov framework empowers community-driven governance, while the use of the Actor Model and WebAssembly (WASM) ensures superior performance over Ethereum’s EVM. Leveraging Rust for smart contract development, Vara Network stands out as a forward-thinking platform poised to shape the future of decentralized technology.
Comparing Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms: PoW vs. PoS vs. NPoS: Why NPoS Leads the Way

Proof of Work (PoW)
How it Works:
Mechanism: Miners compete to solve complex cryptographic puzzles. The first to solve the puzzle adds a new block to the blockchain and is rewarded with new tokens.
Consensus: The security of the network depends on computational power.
Drawbacks:
Energy Consumption: Extremely high energy usage due to continuous computational work. For example, Bitcoin’s energy consumption is comparable to that of entire countries.
Speed and Scalability: Limited transaction throughput due to the time-consuming process of solving puzzles. Bitcoin can handle about 7 transactions per second (TPS), which restricts its scalability.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
How it Works:
Mechanism: Validators are chosen to propose and validate new blocks based on the number of tokens they stake, not computational power.
Consensus: Validators are incentivized to act honestly because their staked tokens are at risk if they attempt fraud.
Advantages:
Energy Efficiency: Requires significantly less energy than PoW, as it doesn’t involve solving complex puzzles.
Scalability: Can handle a higher transaction throughput due to reduced computational requirements. This improves scalability and transaction speed.
Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS)
How it Works:
Mechanism: Divides roles into validators and nominators. Validators secure the network by validating transactions and producing blocks. Nominators delegate their tokens to validators, enhancing the security and decentralization of the network.
Consensus: Validators are selected based on nominations and their performance.
Advantages:
Energy Efficiency: Like PoS, NPoS is energy-efficient and eco-friendly, as it does not involve intensive computations.
Scalability: Provides fast transaction validation and block finality, allowing for higher TPS and better scalability.
Decentralized Participation: Emphasizes community involvement by allowing token holders (nominators) to influence validator selection. This promotes a more democratic and decentralized governance model.
Comparison and Advantages of NPoS Over PoW and PoS:
Energy Consumption: NPoS, like PoS, is far more energy-efficient compared to PoW. It eliminates the need for computational puzzles, leading to a significantly lower carbon footprint.
Transaction Speed and Scalability: NPoS improves scalability and transaction speed more effectively than PoW. It supports higher TPS due to its efficient block production process, making it suitable for large-scale applications.
Decentralized Governance: NPoS offers greater decentralization than PoW and standard PoS systems. By involving nominators in validator selection, it ensures a fairer and more community-driven network governance.
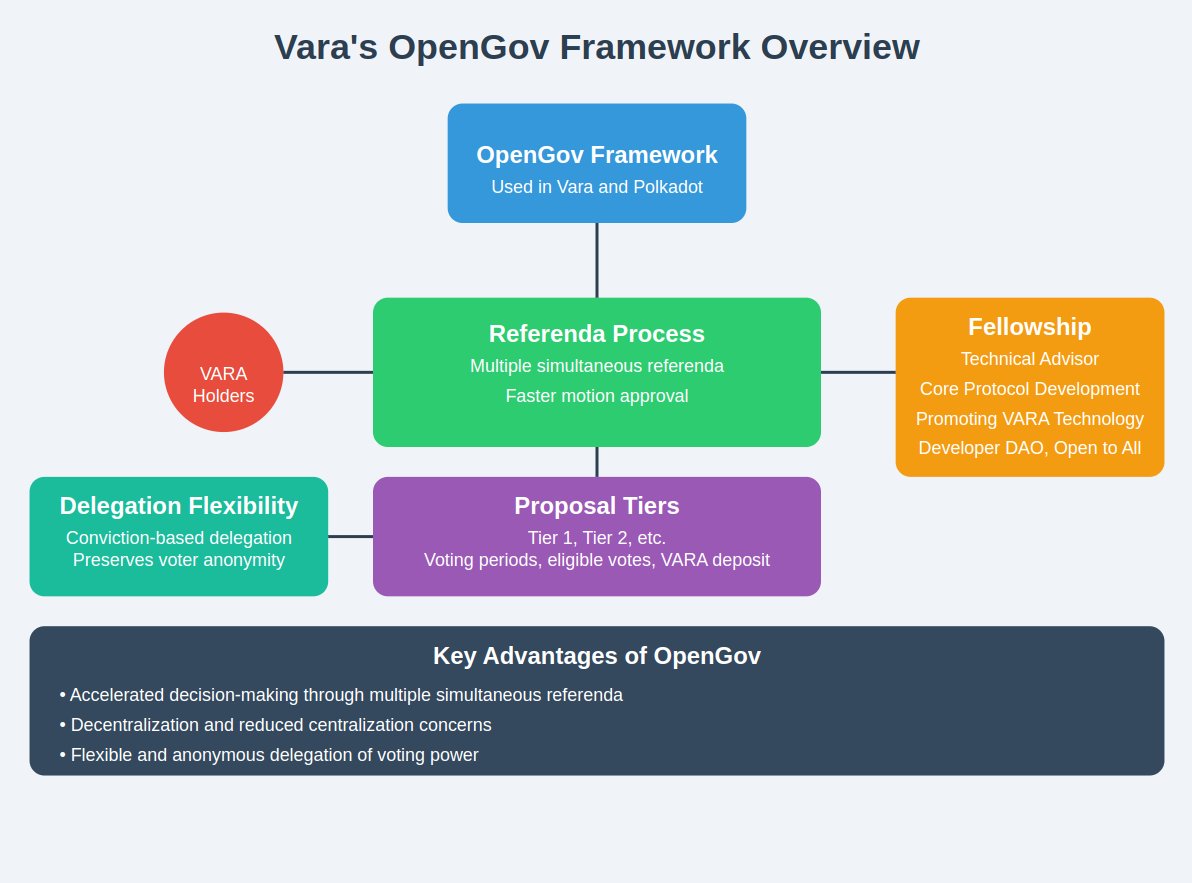
2) Governance: Vara’s OpenGov Framework
Traditional governance in blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum is often controlled by miners or a small group of developers, making it slow and sometimes centralized.
Vara’s OpenGov Framework allows token holders to actively participate in decision-making. This includes network upgrades, treasury allocations, and governance rules.
Why Vara’s governance is better:
Community-driven: Every token holder can vote on important issues.
Decentralized power: No single entity has control, ensuring fair decision-making for the entire ecosystem.
3) Gear Protocol and WebAssembly (WASM) vs. Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
EVM is the standard used by Ethereum and many other blockchains, where developers write smart contracts in Solidity.
Limitations: EVM-based contracts are slower, less efficient, and often limited in flexibility.
Gear Protocol and WebAssembly (WASM) in Vara
WASM is faster and more versatile than EVM. It allows for smart contracts to run at near-native execution speeds.
Gear Protocol is built on WASM, supporting multiple programming languages (like Rust), and enabling complex smart contracts to run smoothly.
Why WASM is better than EVM:
Faster execution: WASM is optimized for speed and performance.
Language flexibility: WASM supports various programming languages, not just Solidity, making it easier for developers from different backgrounds to build on Vara.
4) Actor Model for Communication
Traditional blockchain communication: Most blockchains handle smart contracts and communication using shared memory, which can lead to bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
Vara’s Actor Model: Smart contracts (called actors) operate in isolated environments and communicate asynchronously by passing messages.
Why Vara’s Actor Model is better:
Scalability: Contracts can run concurrently, increasing the network’s capacity to handle transactions.
Efficiency: Message-passing reduces complexity and makes the network faster and more secure.
5) Rust Programming Language vs. Solidity and Move

Solidity (Ethereum) and Move (Aptos, Sui)
Solidity: Ethereum’s primary language is powerful but prone to security vulnerabilities, and it has a steep learning curve.
Move: A newer language used by Aptos and Sui, focused on safety, but still evolving.
Rust in Vara
- Rust is known for its speed, security, and memory safety. It’s a highly performant language that ensures fewer bugs and vulnerabilities.
Why Rust is better than Solidity and Move:
Security: Rust’s strict compiler checks prevent many common coding errors.
Performance: Rust provides fast and efficient code execution, ideal for complex dApps.
Growing developer community: Rust is popular among developers, contributing to its broader use in blockchain development.

Conclusion: Why Vara Stands Out
NPoS consensus ensures faster, more scalable, and energy-efficient blockchain operations compared to PoW.
OpenGov framework promotes true decentralization and active community participation.
Gear Protocol and WASM bring faster, more flexible smart contract execution than EVM.
Actor Model improves scalability and simplifies communication.
Rust offers better security, performance, and developer flexibility compared to Solidity and Move.
Vara Network is designed for the future, solving many of the challenges that older blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum face today. This makes it a powerful platform for the next generation of decentralized applications.